List and Describe the Four Different Generations of Cellular Technology
From this generation the cellular networks became digital. This developed into third generation 3G and now that has advanced into fourth generation 4G and fifth generation 5G.

1g 2g 3g 4g The Evolution Of Wireless Generations
The 5G networks are designed to increase the speed and responsiveness of wireless networks.

. It follows the GSM standards. GSM came before CDMA. Today the 1G 2G 25G and 3G technol ogies is widely using in the e ntire world and.
The second generation 2G is a digital technology and support s text messaging. CDMA is better for large rural areas and was adopted by Verizon and Sprint in the United States. The second generation is the first footstep to digital wireless cellular technology.
The 5G networks are the fifth generation of wireless networks and the latest cellular technology so far. 3rd Generation or 3G was launched at 2003 including HSDPAHSUPAHSPA. Also promises the ability to swap seamlessly between Wi-Fi and wireless phone networks.
List and briefly describe the 4 generations of cellular mobile networks. The first generation 1G mobile wireless communication network was analog used for voice calls only. Streaming was also introduced.
GSM is the global technology. First commercially launched in Finland by Radiolinja now acquired by elisa. Fourth Generation 4G The introduction of 4G went one step further than the revolutionary 3G.
2G 2nd Generation. 1G 2G 3G 4G. In this knowledgebase article we will focus on the evolution and development of various generations of mobile wireless technology along with their significance and advantages of one over the other.
It supported voice and SMS both. Cellular communication is progressing through different generations. All of the names refer to the generation of wireless communications that the technology has gone through.
Its five times faster than the 3G network and can in theory provide speeds of up to 100Mbps. 3 May- June 2016 ISSN - 2320-6349 Different Generations of Cellular Technology- A Survey Waqar Ahmad1 Muhammad Zahid1 Muhammad Irfan1 Habib ur rehman1 Najeeb Muhammad1 1Department of Computer Science Abdul Wali Khan University Madan KPK Pakistan Email. We are currently fully deployed in 4G with 5G gaining ground.
Speed - 64 kbps. Computer Science Engineering Technology Networking MISY 250. Refers to third-generation cellular technology.
Its different from VoLTE because with VoLTE the calls are going over the phone companys network. 1G 2G 3G 4G and 5G. A cellular data network technology that transmits data at speeds up to 100 kbits on a CDMA network.
Capabilities include audio and data transmission using digital signals. 2G WLAN provided high data rate large area coverage. Each generation have some standards different capacities new techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
This is the most common type of network. Supported all 4 sectors of wireless industry namely Digital cellular Mobile Data PCS WLAN Moderate mobile data service. 4G is the first generation to use Long-Term Evolution LTE technology to deliver theoretical download speeds of between 10Mbps and 1Gbps offering end users better latency less buffering improved voice quality instant messaging services and social media quality.
Digital intro encryption GSM CDMA. List and describe the four different generations of cellular technology 1 First from ECONOMICS 10042 at Collegiate High School At Northwest Florida State. The main difference between these two mobile telephone generations is.
Initially we had first generation 1G then second generation 2G. Channel access second-generation systems allow channels to be dynamically shared by a number of users. Researcher continue working on latest communication.
Waqar Ahmad et al IJMCA Vol. 2G 2nd Generation. 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G Error detection and correction second-generation digital traffic allows for detection and correction giving clear voice reception.
In the past few decades mobile wireless technologies have experience 4 or 5 generations of technology revolution and evolution namely from 0G to 4G. Intro higher transfer rates. 1G or 1-G refers to the first generation of wireless telephone technology mobile telecommunications.
The cellular communications networks are known by their numeric generation. 25G came after 2G which used the concept of GPRS. 1st generation of GSM analog technology.
Describe the typical sequence of socket functions for a client socket connect send and receive until done close Describe the typical sequence of socket functions for a server. The second generation or 2G was introduced in 1991 and includes CDMA Code Division Multiple Access that spread across North America Japan and some other markets with high-speed data transmission capabilities. The introduction of 4G really ushered in the era of the smartphone and hand-held mobile device.
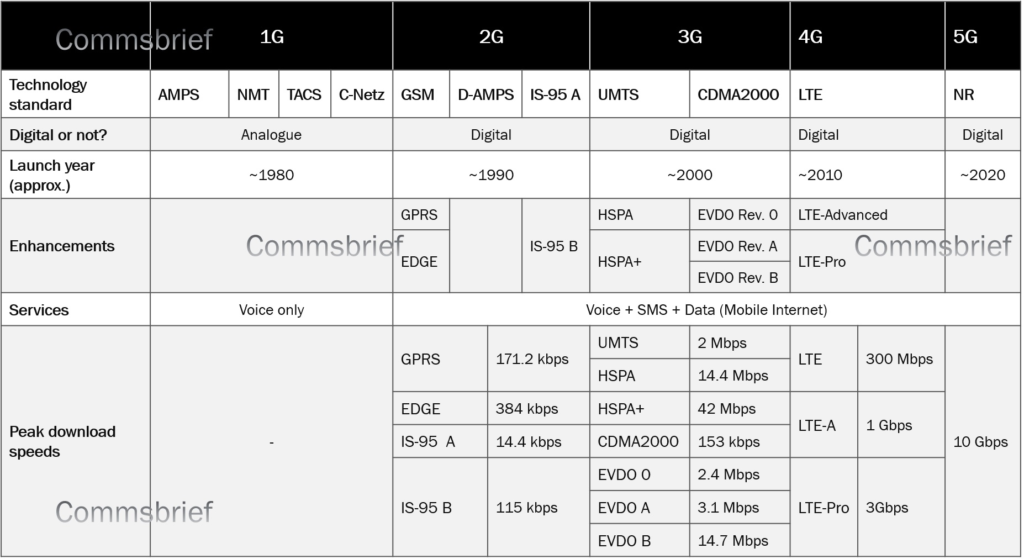
For each generation list the names of the most commonly used standards eg GSM the data rate supported etc. All mobile models released from 2013 onwards should support this network which can offer connectivity for tablets and laptops as well as smartphones. For eg 1G offers 24 kbps 2G offers 64 Kbps and is based on GSM 3G offers 144 kbps-2 mbps whereas 4G offers 100 Mbps - 1 Gbps and is based on LTE technology.
Refers to second-generation cellular technology. Generation 1 is the original GSM technology developed by IBM in 1983. These are the analog telecommunication standards that were introduced in 1979 and the early to mid-1980s and continued until being replaced by 2G digital telecommunications.
List and describe the four different generations of cellular technology 1 First. Shifted from analog to digital. The aim of wireless communication is to provide high quality reliable communication just like wired communicationoptical fibre and each new generation of services represents a big stepa leap.
Mobile internet services provided to external systems laptops wireless modems etc LTE. Generations of Network.

1g 2g 3g 4g The Evolution Of Wireless Generations

From The First To The Fifth Generation Telecommunications Standards

Comments
Post a Comment